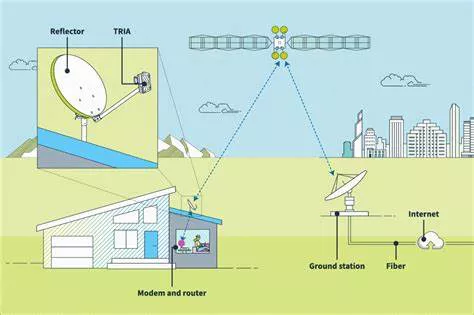
China’s commercial aerospace sector transitions from initial development to rapid expansion
Recent Milestone: Successful Launch of LEO Satellite Group
China recently achieved another successful launch of its low-earth orbit (LEO) satellite internet constellation, deploying the 04 group via a Long March 6A rocket from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center. This marks continued progress in the country’s ambitious satellite internet plans
Industry Analysis: Valuation Expansion Potential
Western Securities highlights that China’s satellite internet sector is entering a phase of accelerated development with significant valuation upside potential.
Key drivers include:
Policy Support: Comprehensive regulations on satellite coordination and private sector participation have established a robust framework
User Growth: Over 2 million Tiantong satellite service subscribers and 16 million terminal devices in use:cite[6].
Technology Readiness: Breakthroughs across satellite manufacturing, launch services, and ground equipment sectors
Market Outlook: From Initial Deployment to Commercial Scale
CITIC Securities analyst Fu Chenshuo notes China’s commercial aerospace sector has completed its “from 0 to 1” foundational phase and now enters rapid development. Huawei’s upcoming public testing of satellite internet services in late 2025 is expected to further drive adoption
Investment Opportunities in Related Companies
| Company | Role in Industry | Key Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Parker Advanced Materials | Specialized component supplier | Precision alloy rings for satellites and rockets |
| Shanghai Hugong | Satellite integration | Commercial satellite AIT (Assembly, Integration, Testing) |
Broader Industry Context
China’s satellite internet strategy involves two major LEO constellations – “Qianfan” and “Star Network” – with plans to launch 700-800 satellites in 2025, a tenfold increase from 2024. The domestic rocket industry’s improving competitiveness, including progress in reusable launch technology, supports this expansion
As the sector transitions from government-led projects to commercial viability, investors are watching for:
- Continued technological breakthroughs in satellite miniaturization and cost reduction
- Expansion of practical applications (e.g., emergency communications, IoT)
- Potential policy catalysts as satellite internet becomes integral to China’s digital infrastructure plans
Related topics: